Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a comprehensive healthcare tradition that dates back over 2,500 years. Currently, one-fourth of the world’s population makes use of it.
Created by some of the best educators and brightest scholars in Chinese history, it is a means of strengthening the body, which can be weakened by modern-day stress and environmental hazards. Chinese Medicine is holistic, taking into account all systems of the body, in order to strengthen vital energy, or qi (pronounced “chee”) so that the body can heal itself.
The cornerstones of TCM are acupuncture and herbal medicine. Chinese Herbal Medicine works in concert with acupuncture; providing the nourishing support for acupuncture’s energetic efforts. In addition, gua sha, moxabustion, cupping and electro acupuncture are adjunctive treatments used in Chinese Medicine.
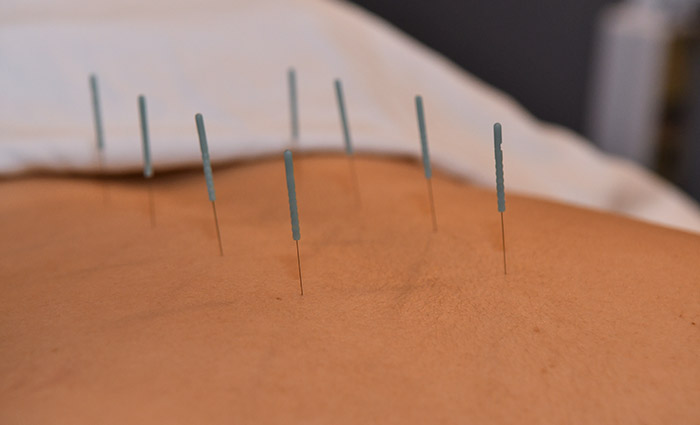
What is Acupuncture?
Acupuncture is the insertion of very fine needles on various points on the body’s surface to influence physiological functioning of the body. Acupuncture mobilizes and regulates qi and blood to invigorate the physiological function of the muscles, nerves, glands and organs.
Adjunctive Therapies – Complementary Therapies
In addition to acupuncture, there are many adjunct/accessory techniques that the acupuncturist may include in the treatment.
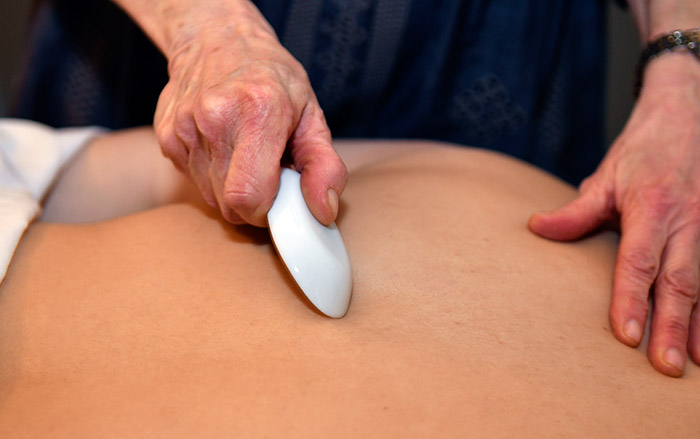
Guasha
Guasha is a technique used to assist in releasing pain and stagnation from the muscles and fascia throughout the body. Guasha can provide immediate relief from pain, stiffness, fever, chill, cough and other symptoms. The practitioner identifies the area(s) that need to be relieved. After applying massage oil to the body, the practitioner uses a round-edged tool, in the shape of a spoon, and rubs it on the chosen area.
The practitioner applies gentle pressure on the body with the spoon; there may be slight discomfort as this is a new sensation. Afterwards, the area will have a reddish hue. If there is intense or moderate stagnation, red dots will color the skin. These “red dots” do not hurt, though the area may be tender. The dots will disappear after 2-to-3 days. The area should be covered and not exposed to sun until the dots fade.
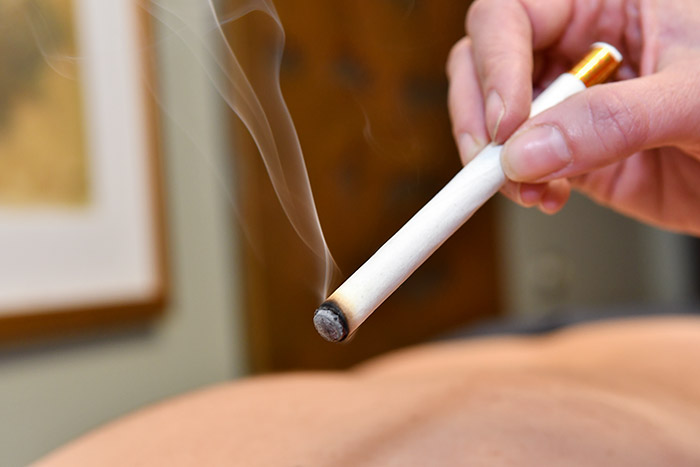
Moxabustion
Moxabustion is a technique that involves the burning of the herb mugwort over specific points on the body, to promote healing. Moxabustion has been used throughout Asia for thousands of years. The translation for the word acupuncture literally means Moxabustion. The purpose of Moxabustion is to strengthen the blood, stimulate the flow of qi and maintain good general health.
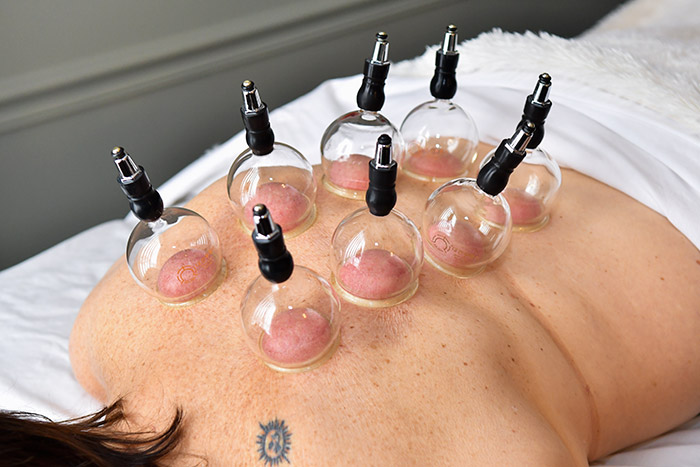
Cupping
Cupping, like guasha, is another method of treating pain and stagnation throughout the body. Using heat, the practitioner creates a vacuum in jars, and then applies the cups to the skin. The purpose of cupping is to draw up the underlying tissue and reduce stagnation. Cups are made of glass and come in many sizes. Cupping can be used to treat arthritic pain, abdominal pain, stomachaches, indigestion, headaches and other ailments.
Electro Acupuncture
Electro acupuncture provides stronger stimulation to the acupuncture treatment and is often utilized with musculoskeletal and pain conditions. Electro acupuncture is used after the needles are in place to strengthen the nature of the qi sensation. It was first utilized in China during the 1930s and is now widely employed throughout the country. With the needles and electro acupuncture in place, a certain frequency is passed through the muscles, increasing the sensation and the effect of qi.
Acupuncture is an effective treatment for many disorders including:
Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Muscle strain and sprain
- Low back pain including sciatica
- Tendonitis and tennis elbow
- Carpal Tunnel
- Neck and shoulder pain
Women’s Health Issues
- Fertility
- Menstrual irregularities
- Peri-menopause/menopause
- Fibroids
- Endometriosis
Auto-immune Disorders
- Chronic fatigue
- Lupus
- Fibromyalgia
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Diarrhea
- Acid reflux
- Constipation
- GERD
- Gas and bloating
Respiratory Disorders
- Allergies
- Colds
- Asthma
- Sinus conditions
Neurological Disorders
- Headaches
- Multiple sclerosis
- Bell’s palsy
Physical and Emotional Issues
- Addictions
- Insomnia
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Side effects of cancer therapy